“Reminder to self regarding routing information: This document is derived from Fortinet KB Articles and covers topics such as accessing FIB/RIB routing data via the CLI, understanding the routing process in FortiGate (route-lookup-process), handling multiple default routes when SD-WAN rules are not the preferred option, and more.”
Routing in FortiGate (route-lookup-process)
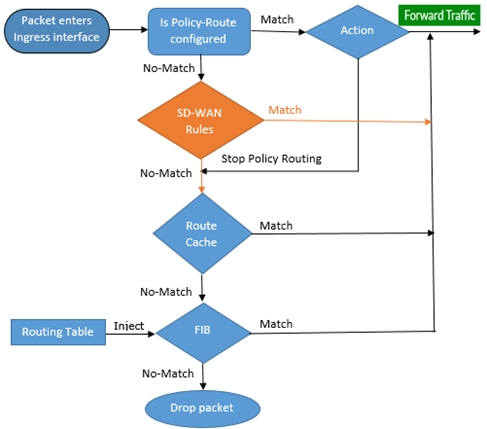
How does FortiGate decide routes?
Viewing FIB/RIB routing information in CLI
RIB vs FIB
Routing Information Base (RIB):
- This is a database of routing prefixes that could potentially be installed into the forwarding table
- RIB is derived from the control plane, it is not used for forwarding. Every protocol such as OSPF, EIGRP, BGP has its own RIB and select their best candidates to try to install to global RIB so that it can then be selected for forwarding.
- The RIB is the input to the route computation.
Forwarding Information Base (FIB)
- It is a table that contains information necessary to forward IP datagrams – ALL active routes in the routing table must be present in the FIB.
- Entries contain interface identifier and next hop information for each reachable destination network prefix.
- The FIB may also include routes that are not in the routing table – such as dynamically added routes to reach SSL-VPN users.
- The FIB is the output of the route computation.
- FIB is derived from RIB
Viewing RIB in CLI
FGT # get router info routing-table all
Codes: K - kernel, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default
C 10.27.0.0/20 is directly connected, port2
C 10.32.0.0/20 is directly connected, port3
C 10.37.0.0/20 is directly connected, port4
O 10.143.0.0/20 [110/2] via 10.27.9.50, port2, 03:53:482 Ways of viewing FIB in CLI
Forwarding table (Kernel routes/FIB)
FGT # get router info kernel
FGT # diagnose ip route list
tab=255 vf=0 scope=253 type=3 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->127.255.255.255/32 pref=127.0.0.1 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=13(root)
tab=255 vf=0 scope=253 type=3 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->169.254.0.64/32 pref=169.254.0.66 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=20(havdlink1)
tab=255 vf=0 scope=254 type=2 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->169.254.0.66/32 pref=169.254.0.66 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=20(havdlink1)
tab=255 vf=0 scope=253 type=3 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->169.254.0.127/32 pref=169.254.0.66 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=20(havdlink1)
tab=254 vf=0 scope=253 type=1 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->10.27.0.0/20 pref=10.27.11.96 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=4(port2)
tab=254 vf=0 scope=253 type=1 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->10.32.0.0/20 pref=10.32.11.96 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=5(port3)
tab=254 vf=0 scope=253 type=1 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->10.37.0.0/20 pref=10.37.11.96 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=6(port4)
tab=254 vf=0 scope=0 type=1 proto=11 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->10.143.0.0/20 pref=0.0.0.0 gwy=10.27.9.50 dev=4(port2)
tab=254 vf=0 scope=253 type=1 proto=2 prio=0 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0->169.254.0.64/26 pref=169.254.0.66 gwy=0.0.0.0 dev=20(havdlink1)FIB Type ID: Type of routing connection
| Type ID | Value |
| 1 | Unicast |
| 2 | Local |
| 3 | Broadcast |
| 4 | Anycast |
| 5 | Multicast |
| 6 | Blackhole |
| 7 | Unreachable |
| 8 | Prohibited |
FIB Proto ID: This indicates where the route came from
| Proto ID | Source Protocol |
| 2 | Kernel |
| 11 | ZebOS |
| 14 | FortiOS |
| 15 | HA |
| 16 | Authentication-based |
| 17 | HA1 |
| 18 | HA Kernel Routes |
FIB Other Values
| tab= | table number (255 for unicast and 254 for multicast) |
| vf= | VDOM index number |
| prio= | Priority of the route, lower priorities are preferred |
| pref= | Preferred next hop |
| gwy= | Address of the gateway for the route |
| dev= | Outgoing interface index |
Links
- FortiGate – Viewing FIB/RIB routing information in CLI
- https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Technical-Tip-FortiGate-Viewing-FIB-RIB-routing-information-in/ta-p/201496
- Routing in FortiGate (route-lookup-process)
- https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Technical-Tip-Routing-in-FortiGate-route-lookup-process/ta-p/194047?externalID=FD50169
- Controlling how HA synchronizes routing table updates
- https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Technical-Tip-Controlling-how-HA-synchronizes-routing-table/ta-p/191310?externalID=10462
- Multiple default routes where SD-WAN rules are not preferred
- https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Technical-Tip-Multiple-default-routes-where-SD-WAN-rules-are-not/ta-p/196237?externalID=FD47747
Photo by Taylor Vick on Unsplash

